Translation memory - Default search settings
In order to have the results refined per resource, you will need to play with the settings highlighted in each resource profile.
The global settings for your platform will define how your segments will be handled in the whole system.
If you do not know how to access the TM settings of a specific resource, see the previous article: Translation memory settings.
Default TM content filtering
After you have opened the Search settings of specific translation memory (or project memory, termbase), you can use the Content filtering options to define how this memory should behave with respect to other translation memories.
When you doubt the content quality of your resource, move the sliders of the pre-translation and penalty settings into the red area. Higher penalties will show only very similar results. Blue coloured values indicate default settings.
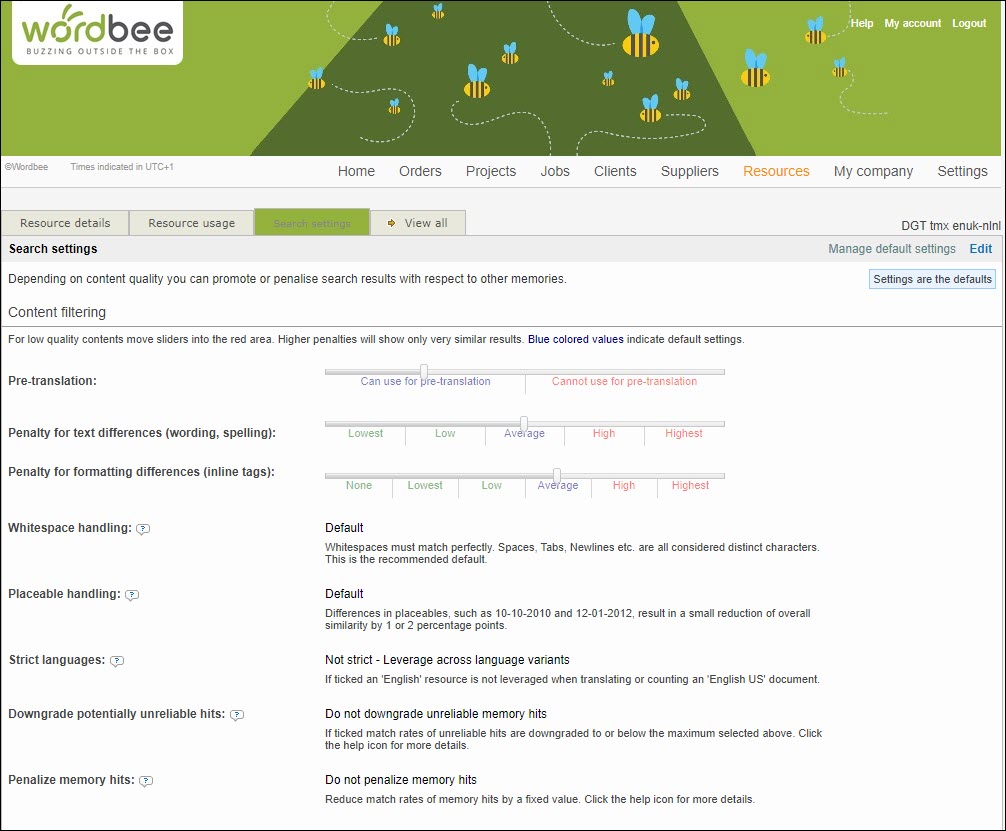
Expand the options below to learn more:
Default translation filters
If you want to hide the default visibility of specific segments so you can guide users to better results available, you can customize the following filters:
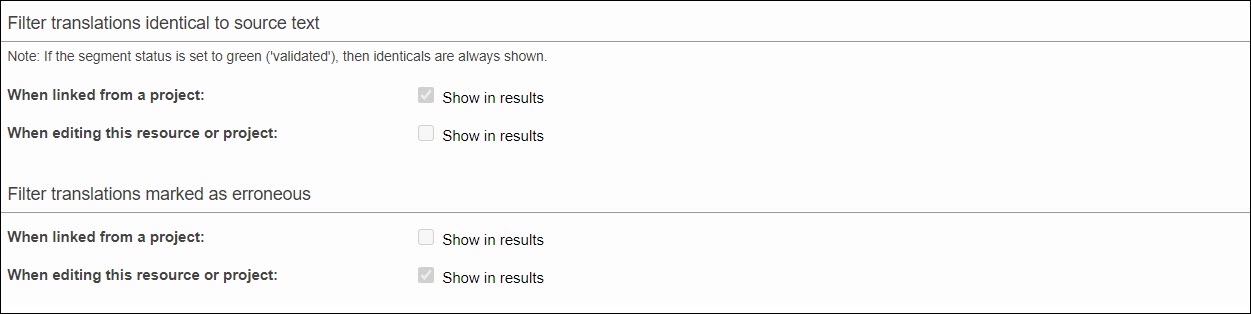
Expand the options below to learn more:
Options like "Show translations identical to source" or "Show translations marked as erroneous (red status)" are available for all resource types: TMs, TBs, and Project Memory.
Learn more
Go back to the platform customization to learn about other settings that you can customize:
